Products Category
Contact Us
Name: Eva Chen
Tel: 0512-65496212
Mobile: +86-13584808209
E-mail: [email protected]
Add: No 1200 ,Xiangcheng Dadao Rd,Xiangcheng District ,Suzhou,China
Skype: Kitty080212
QQ:
2379540141



FAQ
1.How do the commutator and carbon brsuh work?
Jun 8th, 2016 9:22:53 AM
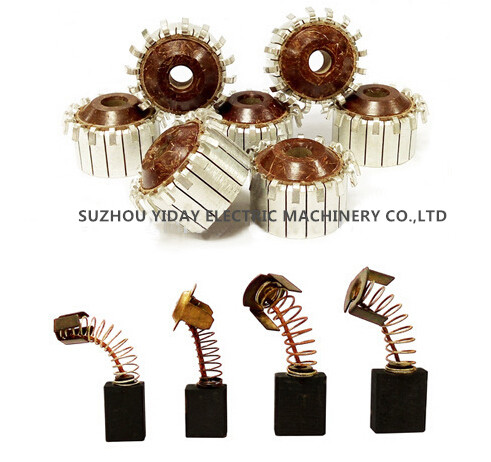

A single commutator bar is a piece of copper connected to one end of an armature coil. Two commutator bars for each coil, are attached to opposite sides of the shaft.Electrical connection is made by pressing carbon brushes against the commutator bars, this allows the shaft to rotate while making electrical connections when the copper bars are in contatct with a carbon brush.
Two carbon brushes are used , one positive and the other negative polarity. At some point in the rotation of the shaft the copper bars that are attached to the coil are in a position such that each copper bar is under one of the carbon brushes. A positve brush electrically connects to a copper bar on the commutator and electricity flows from the positive power supply through the carbon brush and into the copper bar that is underneth it. Power continues to flow from the copper bar via the wire connected to is and into the coil. At the other end of the coil the power leaves passes through a wire and the other copper bar and returns to the negatve power supply connection via the negative brush completing the electrical connection.
As the shaft rotates the copper bars move underneth the brushes to establish an electrical connection and as the rotation continues this electrical connection breaks as the copper bars move out from being underneth. As the shaft continues to rotate the copper bars again come in to contact with the brushes and re-establish an electrical connection. But now these copper bars are connecting to the opposite polarity brushes since the shaft at this point has only revolved 1/2 of a turn.
Look at it another way lets label the copper bars A & B and the Carbon Brushes POS & NEG. Initally the "A" copper bar is connected to the POS brush and B to the NEG brush. The shaft revolves 1/4 turn and no electrical connect is made as the "A" copper bar is inbetween the POS & NEG brushes (as is the B bar as well). The shaft continues to move due to its momentium and the "A" copper bar approaches the NEG brush as the shaft continues to revolve and eventually establishes electrical contact. At the same time the B copper bar is making contact with the POS brush.
Two carbon brushes are used , one positive and the other negative polarity. At some point in the rotation of the shaft the copper bars that are attached to the coil are in a position such that each copper bar is under one of the carbon brushes. A positve brush electrically connects to a copper bar on the commutator and electricity flows from the positive power supply through the carbon brush and into the copper bar that is underneth it. Power continues to flow from the copper bar via the wire connected to is and into the coil. At the other end of the coil the power leaves passes through a wire and the other copper bar and returns to the negatve power supply connection via the negative brush completing the electrical connection.
As the shaft rotates the copper bars move underneth the brushes to establish an electrical connection and as the rotation continues this electrical connection breaks as the copper bars move out from being underneth. As the shaft continues to rotate the copper bars again come in to contact with the brushes and re-establish an electrical connection. But now these copper bars are connecting to the opposite polarity brushes since the shaft at this point has only revolved 1/2 of a turn.
Look at it another way lets label the copper bars A & B and the Carbon Brushes POS & NEG. Initally the "A" copper bar is connected to the POS brush and B to the NEG brush. The shaft revolves 1/4 turn and no electrical connect is made as the "A" copper bar is inbetween the POS & NEG brushes (as is the B bar as well). The shaft continues to move due to its momentium and the "A" copper bar approaches the NEG brush as the shaft continues to revolve and eventually establishes electrical contact. At the same time the B copper bar is making contact with the POS brush.
|
Total: 1
Page: 1 / 1
First
←Previous
Next→
End
|




 Electric ball Valve
Electric ball Valve Solenoid Valve
Solenoid Valve